All of the following factors are low-risk factors in the development of dental caries for adults except one. Any fermentable carbohydrate used frequently will encourage dental caries in some caries-prone subjects.
Sugars in food and drinks play a major role in the development of dental caries.

. All of these choices are correct. Caries can occur in absence of proteolytic organisms. Consumption of dietary carbohydrates is one of the most important etiological factors as they are processed by bacteria in the dental plaque via the glycolytic pathway producing acids mainly lactate Konig and Navia 1995.
The anti-cariogenic effect of fluoride is well documented. Dental caries occurs due to the demineralization of enamel and dentin the hard tissues of the teeth by organic acids formed by bacteria in dental plaque through the anaerobic metabolism of sugars and other fermentable carbohydrates derived from the diet Organic acids increase the solubility of calcium hydroxyapatite in dental hard. Therapies that provide arginine as a substrate for alkali production in supragingival oral biofilms have strong anticaries potential.
Carbohydrates promote dental caries by which of the following mechanisms. Bacteria metabolize carbohydrate to form acids which break down enamel Carbohydrates provide 60 percent of the energy in Jimmy Johns diet of 2700 kilocalories. 11 The dental caries process.
Carbohydrates promote dental caries by which of the following mechanisms. 1 extracellular polysaccharides eps which promote bacterial accumulation to the tooth surface and influence the physical and biochemical properties of biofilms. The most important cause of dental caries is the frequency of intake of fermentable carbohydrates which supply substrate to the caries-producing oral bacteria.
The nature of the oral cavity and host behaviors has mandated that the oral microbiota evolve mechanisms for coping with environmental fluctuations especially changes in the type and availability of carbohydrates. All of these choices are correct. Glucose sucrose fructose or cooked starch acids are generated as a by-product.
1 and sugars as well as salivary and genetic influences. Sugar promotes the growth of bacteria that breakdown enamel. 1 these acids diffuse through the biofilm and into the porous enamel dissolving calcium phosphate mineral from the tooth surface.
However Proteolytic bacteria are rare in oral cavity No explanation for role of carbohydrates acid etc in dental caries Carious lesions cannot be reproduced in vitro by the proteolytic mechanisms Gnotobiotic studies. The potential for caries exists every time a carbohydrate is eaten because most foods promote acid formation if no procedures are taken to remove food debris or plaque biofilm to buffer the acid produced. Carbohydrates stick to teeth preventing the removal of plaque.
We extend the assertion from other investigators that lactobacilli found in the GI tract originate in the oral cavity by proposing that lactobacilli in the oral cavity arise from caries lesions. Fluoride and the frequency of ingestion of fermentable carbohydrates are the two greatest issues in the fight against dental caries. Up to 24 cash back An individual can be in the high-risk or low-riskcategory for development of dental caries.
Dental caries is a disease with a multifactorial etiology. However other individuals will experience. Frequent and prolonged exposure of the teeth to dietary carbohydrates generates an acidic.
Caries lesions develop when acid production from bacterial metabolism of dietary carbohydrates outweighs the various mechanisms that promote pH homeostasis including bacterial alkali production. Increases the thickness of gold. Residents are exposed to fluoride to some degree only 58 percent receive optimal levels through community water systems.
Dental caries involves in teractions between the tooth structure the microbial biofilm formed on the tooth sur face FIG. Sugar and tooth decay. Bacteria metabolize carbohydrate to form acids which break down enamel.
It is now well known that not all individuals are susceptible to dental decay to the same degree so the use of dietary carbohydrate will not bring about the same prevalence of decay in all people. Bacteria within the plaque use the sugar as energy and release acid as a waste product which gradually dissolves the enamel in the teeth 1. The tooth preparation for a porcelain veneer must have aan A 45 year old patient has 32 unrestored teeth.
Lactobacilli present in caries lesions represent both a major contributor to caries progression and a major reservoir to the gastrointestinal GI tract. The polysaccharides in biofilms can be divided into two categories. Sugar promotes the growth of bacteria that breakdown enamel.
Bacteria metabolize carbohydrate to form acids which break down enamel. Although sugars are undoubtedly the most important dietary factors in the etiology of dental caries todays diet contains an increasing range of fermentable carbohydrates including highly processed starch-containing foods and foods that contain novel synthetic carbohydrates such as oligofructose sucralose and glucose polymers. When biofilm bacteria such as mutans streptococci metabolize fermentable carbohydrates ie.
Carbohydrates promote dental caries by which of the following mechanisms. Test Bank Course Title. And 2 intracellular polysaccharides ips which serve as an endogenous source of carbohydrates that can be.
1 this process of mineral loss at the. View Test Prep - Chapter 4 from NHM 311 at University of Mississippi. Carbohydrates stick to teeth preventing the removal of plaque.
In the case of human dental caries the presence of excess carbohydrates is often responsible for altering the local environment to be. For a cast gold restoration a gingival bevel is used instead of a shoulder because a bevel 1.

Dietary Carbohydrate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Factors In Caries Development And The Balance Between Pathological Download Scientific Diagram

Positive Feedback Loop Leading To Caries In This Positive Feedback Download Scientific Diagram
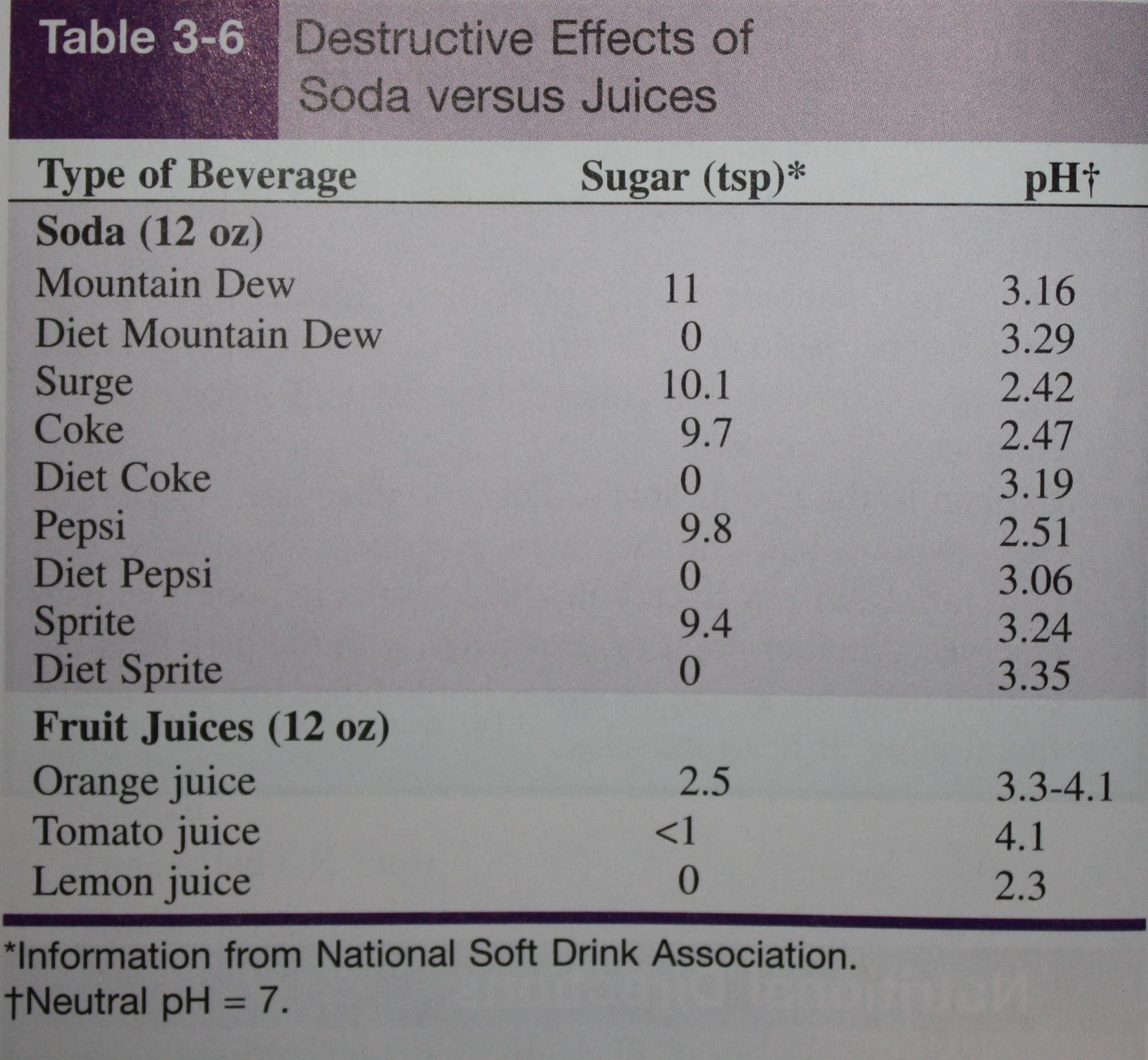
0 Comments